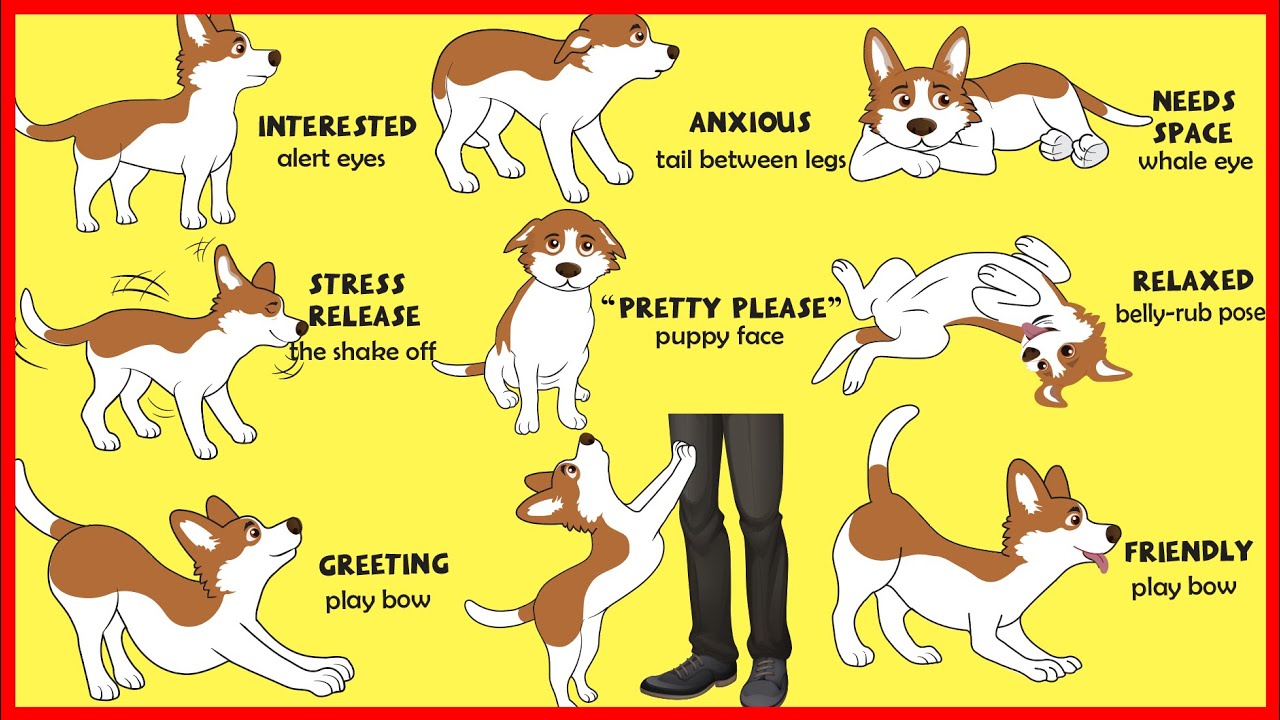
Understanding Dog Body Language: Signs and Meanings
Dogs communicate primarily through body language, using a combination of facial expressions, posture, and gestures to convey their emotions, intentions, and needs. Understanding your dog's body language can strengthen your bond and prevent misunderstandings. Here are some key signs to watch for and their meanings:
Tail Wagging: Contrary to popular belief, a wagging tail doesn't always indicate happiness. The speed, height, and direction of the wag can convey different emotions. A high, fast wag may signal excitement or arousal, while a low, slow wag could indicate insecurity or anxiety.
Ears: The position and movement of a dog's ears can provide insight into their mood. Forward-facing ears usually indicate alertness or interest, while flattened ears suggest fear or submission. A relaxed dog may have their ears in a neutral position.
Body Posture: A dog's overall body posture can convey confidence, fear, aggression, or relaxation. A confident dog may stand tall with their head held high and tail erect, while a fearful or submissive dog may cower or try to make themselves appear smaller.
Eye Contact: Direct eye contact can be perceived as threatening or confrontational in dog language. A soft gaze or gentle blinking is often a sign of trust and relaxation, while a fixed stare may indicate aggression or discomfort.
Lip Licking and Yawning: Dogs may lick their lips or yawn in stressful situations as a way to alleviate tension. These behaviors can signal anxiety, discomfort, or a desire to diffuse a potentially tense situation.
Paw Raises: A dog lifting one paw can be a sign of uncertainty or a request for attention. It's often seen during greetings or when a dog is unsure about a situation.
Growling and Snarling: Vocalizations such as growling or snarling are clear indicators of discomfort, fear, or aggression. It's essential to respect a dog's warning signals and avoid escalating the situation.
By paying attention to these subtle cues and body language signals, you can better understand your dog's emotions and respond appropriately to their needs.